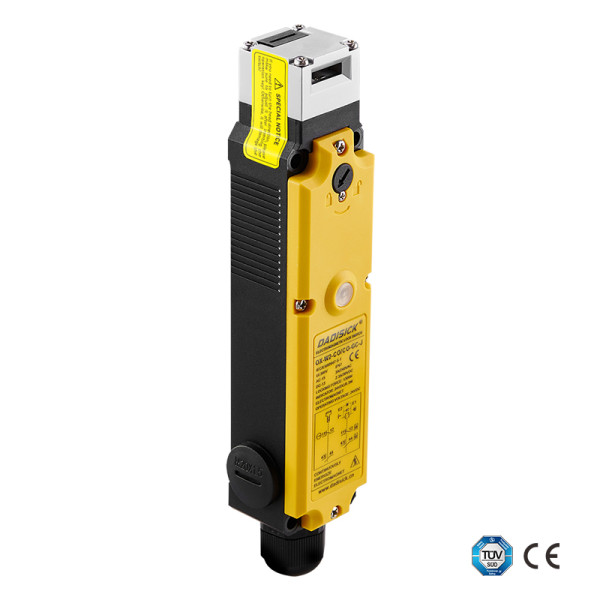
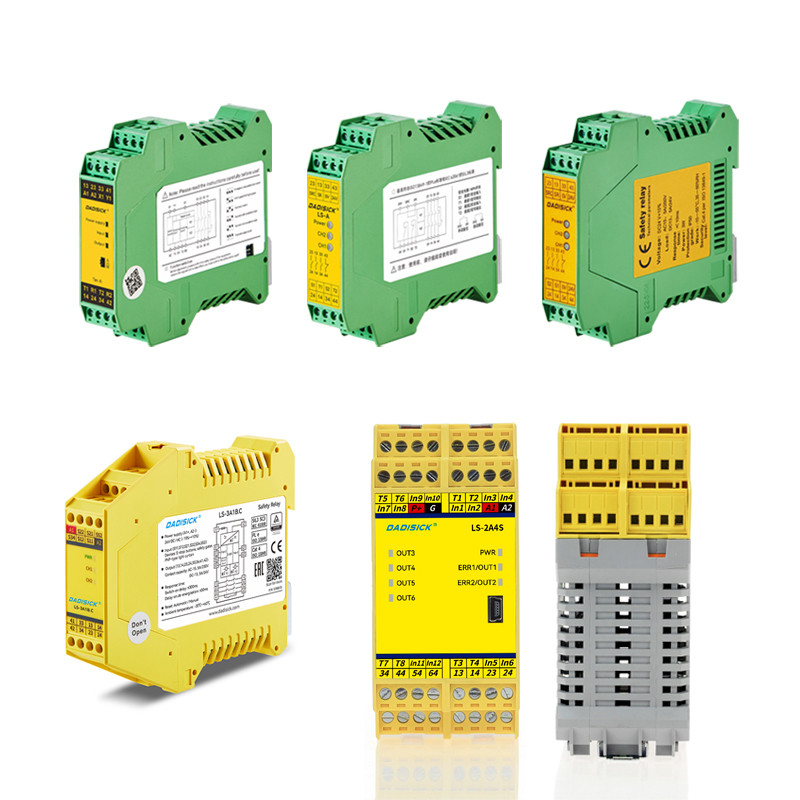
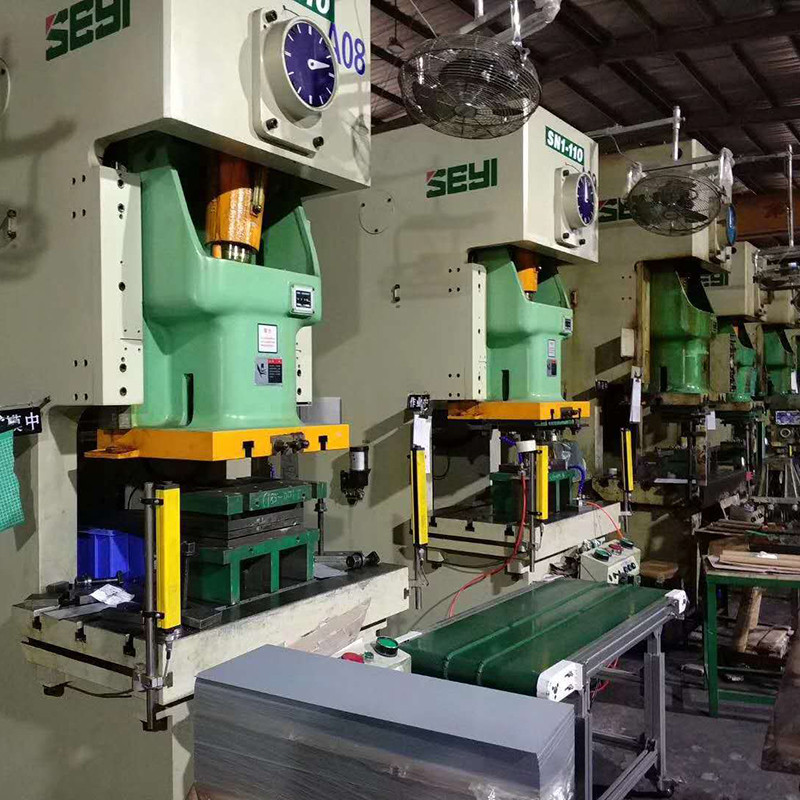
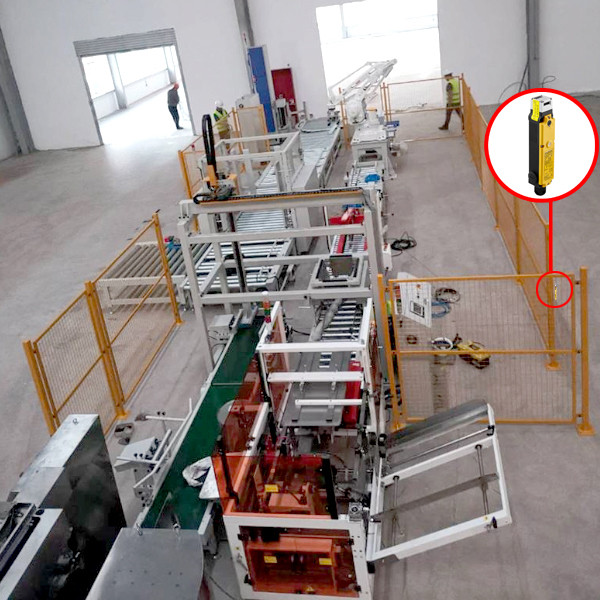
DADISICK has always been committed to high-end security sensor products, focusing on technological research and development and product innovation. Our products are widely used in industries such as automation equipment, mechanical manufacturing, automobile manufacturing, and electronics manufacturing, helping to reduce the rate of industrial accidents and ensure employee safety. We continue to introduce new products that meet market demands, providing support for enterprise safety production.
*Replacement Services:In a highly competitive market, businesses need to continually improve their products to maintain market share. We provide safety sensor replacement services.
*Improving or adjusting product lines:When a company enters new markets or shifts focus, it may need to refine its product line. We offer safety sensor products and technical support for this transition.
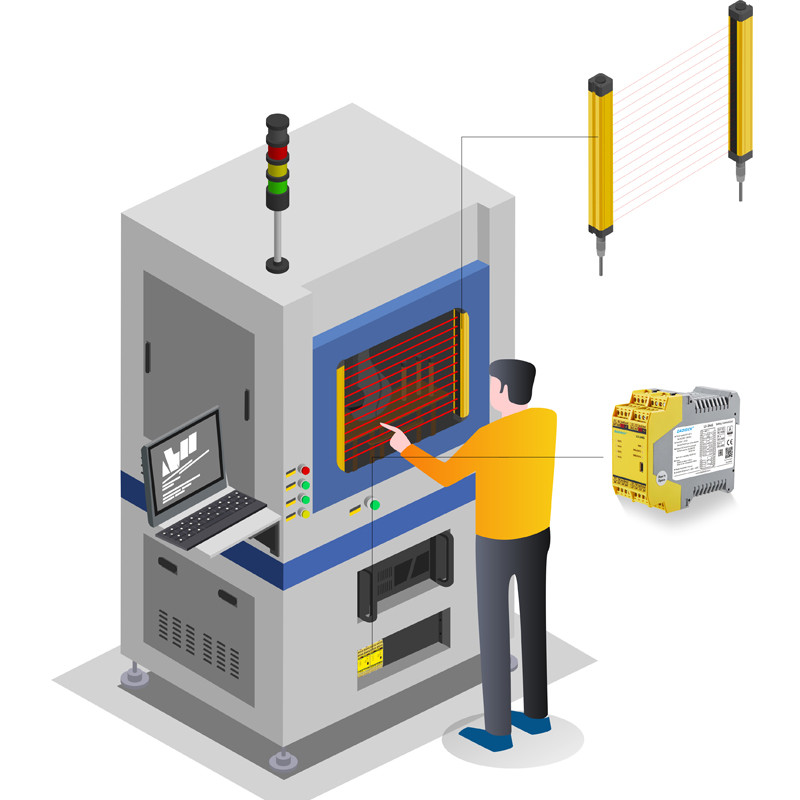
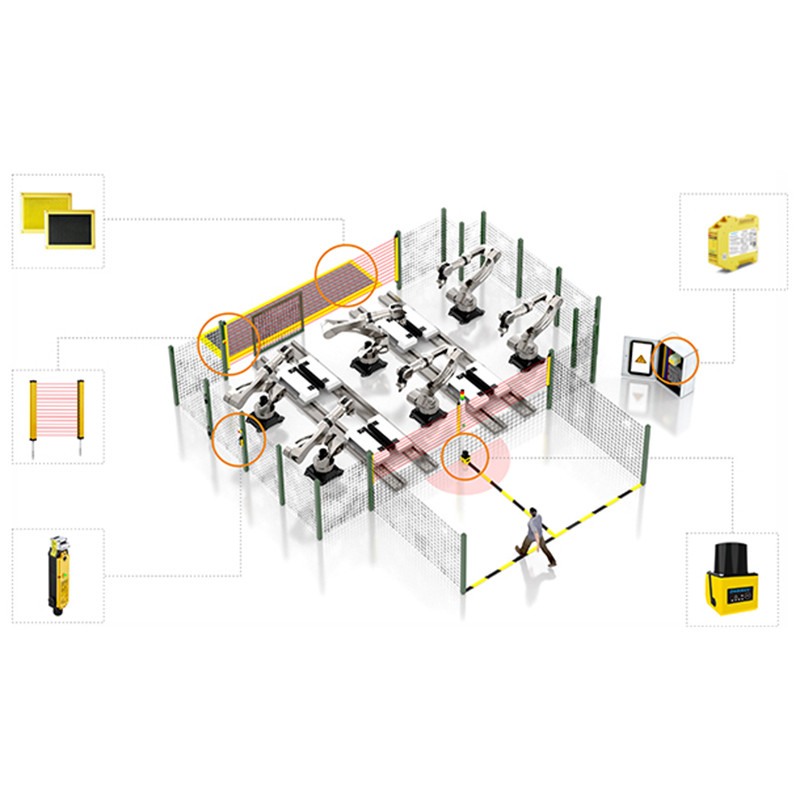
*Automation IndustryMonitor equipment operation status, promptly halt or adjust machine actions to ensure production process safety.
*Mechanical ManufacturingMonitor mechanical motion components, prevent potential hazards, safeguard employee safety and production line smooth operation.
*Automotive ManufacturingSafety monitor high-risk processes on vehicle assembly lines, enhance worker safety and production efficiency.
*Chemical IndustryReal-time monitoring of production environment, ensure safety in handling toxic and hazardous substances.
*Food and Beverage IndustryMonitor production line equipment operation, prevent food contamination and waste.
*Logistics and WarehousingUsed for AGV navigation and obstacle avoidance, ensure safe transportation of goods.
*Wood Processing, Textile, Papermaking, Printing, Rubber, and Plastic industries, among others, safety sensors are used to monitor various production processes, ensuring safety and efficiency.