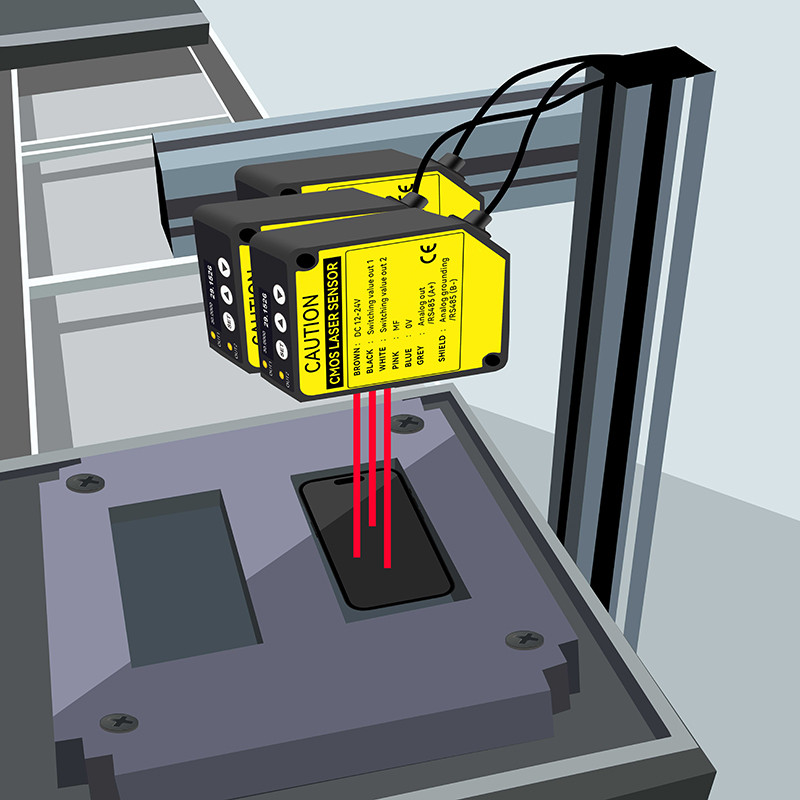
What is A Contact Type Displacement Sensor?
What is A Contact Type Displacement Sensor?
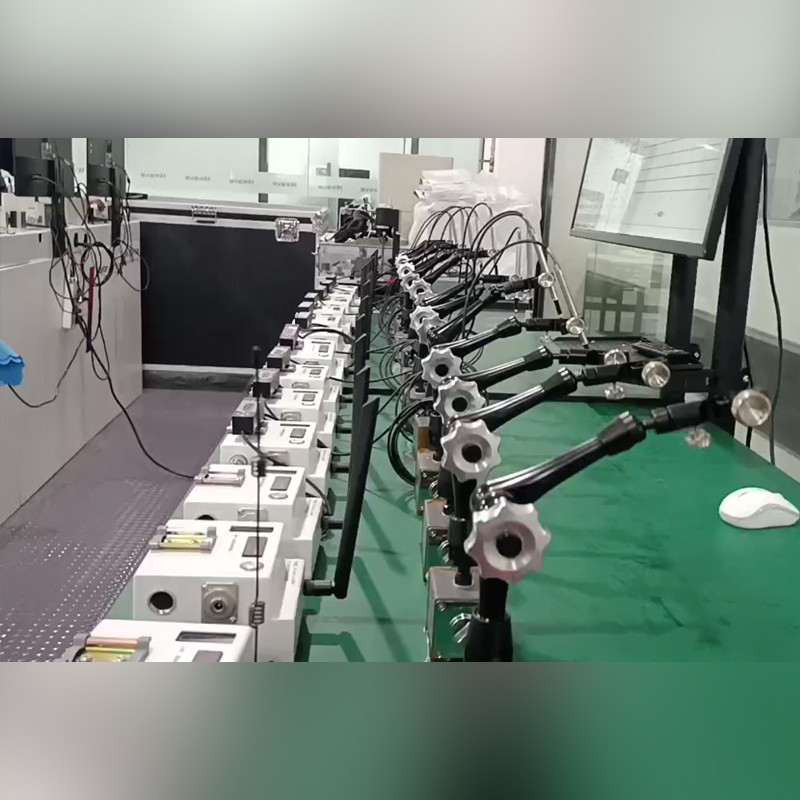
Contact Displacement Sensors
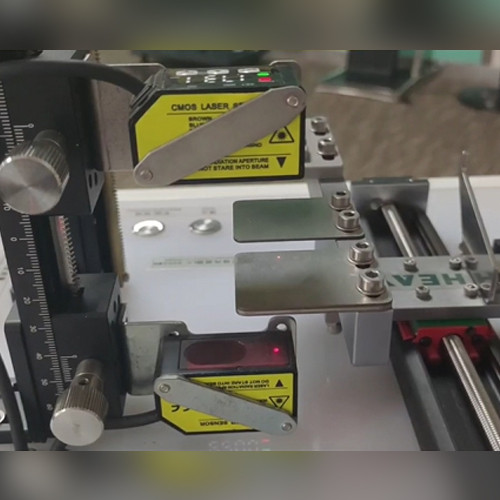
How Do Contact Type Displacement Sensors Work?
Working Principle of Contact Displacement Sensors
How to Choose the Right Contact Displacement Sensor?
Key Points for Selecting Contact Displacement Sensors
Differences Between Contact Displacement Sensors and Non-Contact Displacement Sensors
| Comparison Dimension | Contact Displacement Sensors | Non-Contact Displacement Sensors | ||
| Measurement Method | Requires direct contact with the object | Indirect measurement via electromagnetic waves, laser, etc. | ||
| Accuracy and Stability | High precision (micron/nanometer level) | Sensitive to ambient light and surface material | ||
| Durability | Prone to wear, requires regular maintenance | Long lifespan (no physical contact) | ||
Applicable Scenarios | Precision machining, static or low-speed measurements | High-speed moving objects, detection of fragile surfaces | ||